Math 9 CHAPTER 7 BEARINGS and TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
50º 55º 60º 65º If the height of a pole is 2\sqrt3 2 3 metres and the length of its shadow is 2 2 metres, then find the angle of elevation of the sun. Word Problems It is often useful to draw a diagram and remember how the basic trigonometric functions relate the angles and measurements of sides in a right triangle.

Trigonometry and Bearings Overview ( Video ) Trigonometry CK12 Foundation
Trigonometry and Bearings. Pythagoras Theorem. Pythagoras Theorem and Trigonometric Ratios. Using Trigonometric Ratios to calculate angles and sides. The Sine Rule. The Cosine Rule. Bearings Part 1. The Fundamentals. Bearings part 2. Proudly powered by.

How to Calculate a Bearing Using Trigonometry YouTube
The full lesson and more can be found on our website at https://mathsathome.com/calculating-bearingsIn this lesson we learn how to find a bearing using trigo.

Bearings with trigonometry Teaching Resources
To find the bearing, you can use basic geometry (usually involving right-angled triangles) and trigonometry. The cosine rule, sine rule or Pythagoras' theorem might also be used, depending on the problem. Remember that sine, cosine, and tangent apply to right-angled triangles - sin = opposite/hypotenuse, cos = adjacent/hypotenuse, and tan.

Trigonometry Questions With Bearings
College Trigonometry Trigonometric Functions graphs, Inverse Trigonometric Functions Applications of Trigonometric Functions Solve Problems Involving Bearings 0m:0s Trigonometry with Bearings Heather Whitehead 324 Was this helpful? Previous video Comments (0) Flying with a bearing application with trigonometric function 343 11:18

Bearings with trigonometry (SOHCAHTOA) Teaching Resources
The bearing needed is the angle marked with the blue arc. It is clockwise from north. 2. Use trigonometry to write an equation and solve it for θ, the bearing. 3km is opposite θ. 6km is adjacent to θ. So the trig ratio we need is tan.
[0272] Trigonometry Finding Bearings and Distances (Example 1) YouTube
PPT Standard PDF Small PDF Calculating Bearings Choosing a Trigonometric Ratio to Use Calculating Angles & Lengths Using Trigonometry Angles of Elevation & Depression Solving Real-Life Problems Using Trigonometry 3D Trigonometry Problems Ready-to-use mathematics resources for Key Stage 3, Key Stage 4 and GCSE maths classes.

E Maths Chap 3.8 Further Trigonometry Bearings Example 2 YouTube
Trigonometry 4 units · 36 skills. Unit 1 Right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 2 Trigonometric functions. Unit 3 Non-right triangles & trigonometry. Unit 4 Trigonometric equations and identities. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course. Start Course challenge. Math.

Right Triangles and Bearings ( Video ) Trigonometry CK12 Foundation
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Bearings. Videos, worksheets, 5-a-day and much more

how to solve Bearings with Trigonometry YouTube
Use bearings with trigonometry to find a distance or direction Key ideas Bearings tell us the direction, on a map, of one point from another. Bearings are always measured clockwise from a line pointing north. Bearings are usually written as three-figure bearings. For example, 070° means 70°. The word "from" is really important.

Use of bearings and finding an angle using trigonometry YouTube
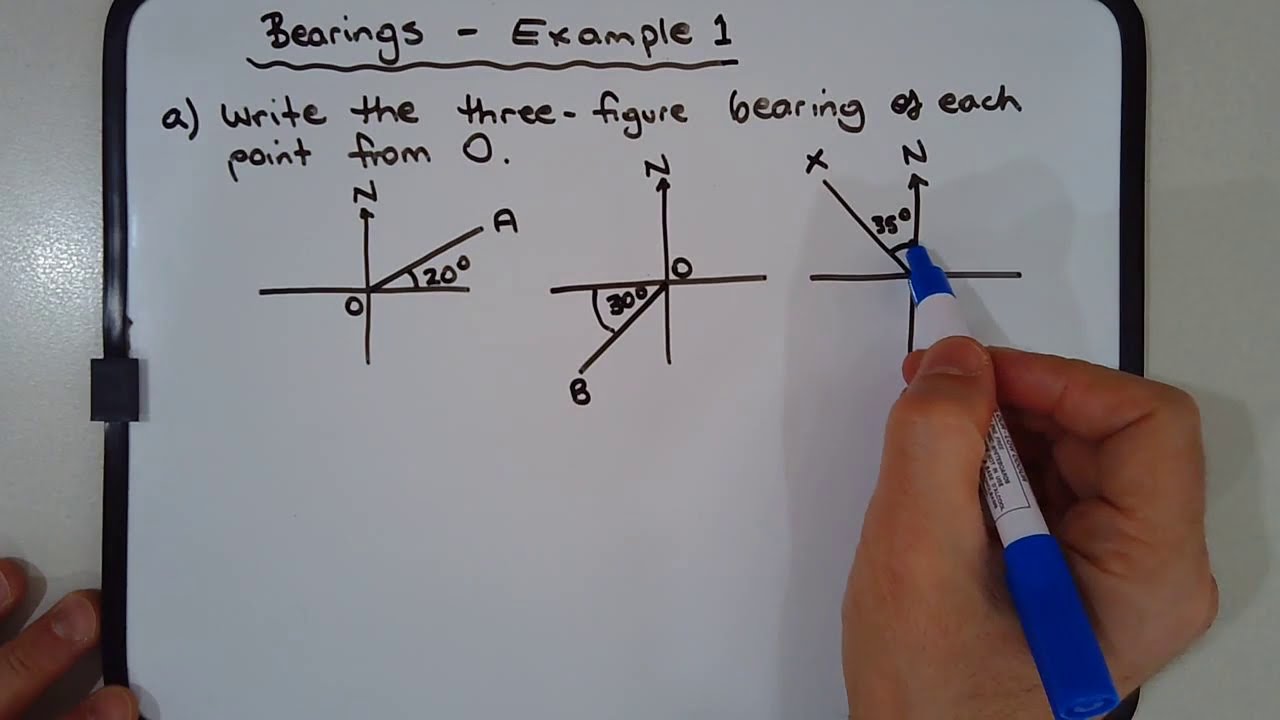
3 rules of bearings. Bearings are measured from the North line. Bearings are measured in the clockwise direction. Bearings are expressed with 3-figures so 65∘ becomes 065∘ . ⇒ start from B (so draw a north line at B). E.g. 1 Write down the bearing of A from B . N.B. "Start from B " so there must be a north arrow at B .

Bearings Trigonometry Problem with Cosine Rule and Sine Rule Exam Question Solved YouTube
Bearing - Trigonometry . Because the angle begins in the south direction and moves towards the west, the correct bearing is To solve this problem, begin with a diagram, and label all known information. We know that we can label two angles as By alternate interior angles, the other diagrammed angle will also be equal to
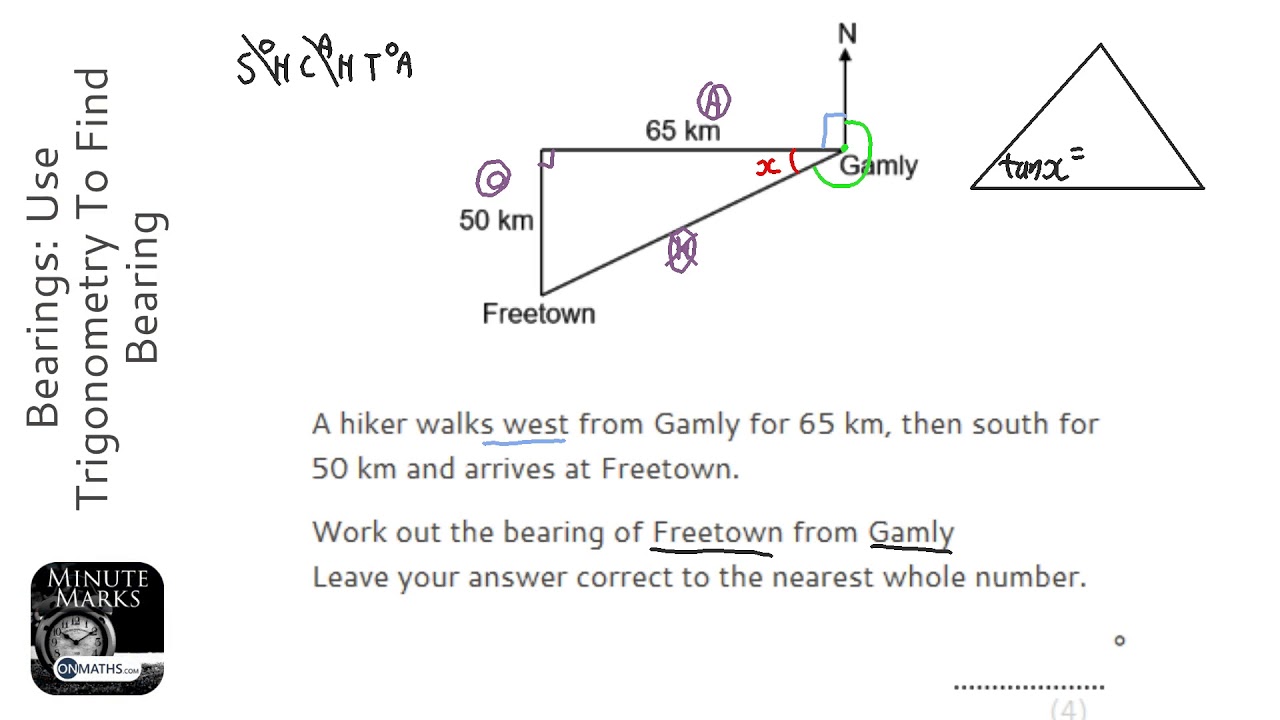
Bearings Use Trigonometry To Find Bearing (Grade 5) OnMaths GCSE Maths Revision YouTube
Calculate a Bearing Using Trigonometry: Video Lesson What is a Bearing in Mathematics? In mathematics, a bearing is defined as an angle measured clockwise from north. Bearings are usually written as a three-figure bearing. For example, the angle 50° from north is written as 050°. A bearing is always defined as an angle clockwise from north.

Trigonometry with Bearings YouTube
Developing learners will be able to calculate the size of a bearing using trigonometry. Secure learners will be able to find missing lengths in bearings problems using trigonometry. Excelling learners will be able to solve unfamiliar problems by combining the use of bearings and trigonometry. Main: Walked through examples and practice questions.
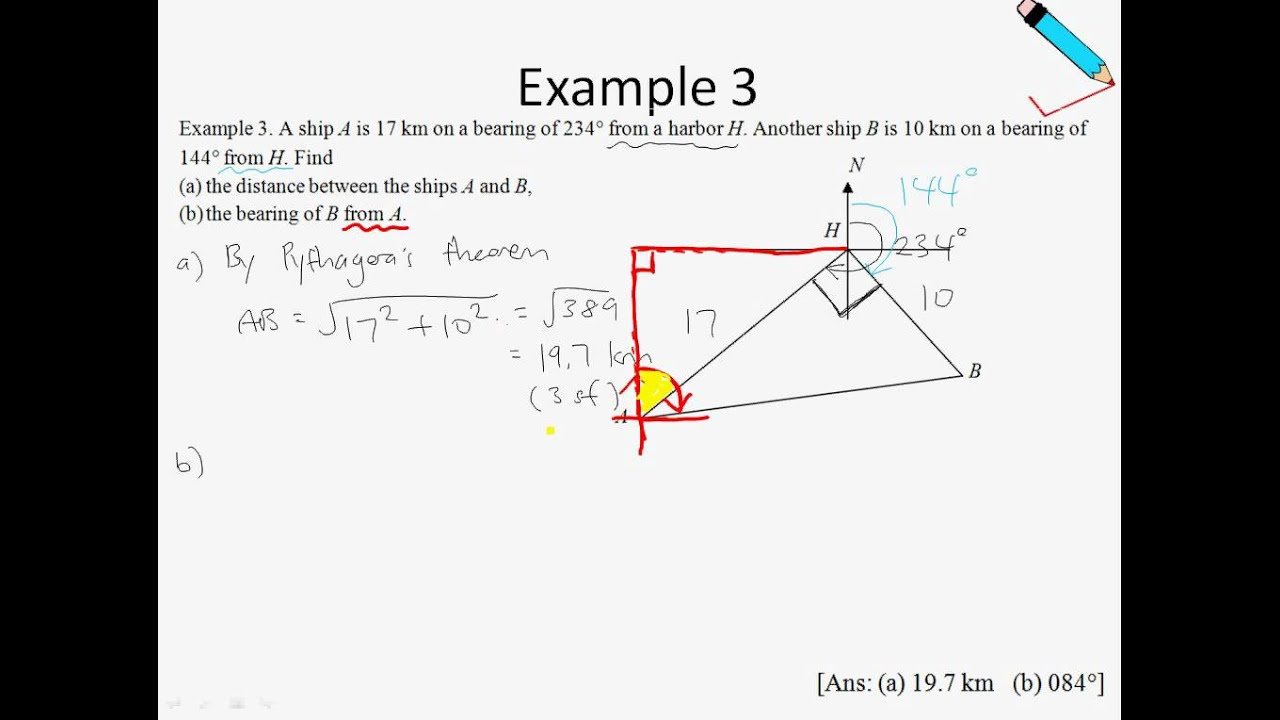
E Maths Chap 3.8 Further Trigonometry Bearings Example 3 YouTube
A collection of videos, games, activities and worksheets that are suitable for GCSE Maths. 3 figure bearings GCSE basics. Bearings 1 (GCSE Higher Maths) Show Video. Bearings 2 (GCSE Higher Maths)- Exam Questions. Cosine Rule and Bearing Problem - GCSE and a-level revision video. This video shows how to use the cosine rule to solve a problem.

Bearings Use Trigonometry To Find Bearing (Grade 5) OnMaths GCSE Maths Revision YouTube
Bearings A bearing is an angle, measured clockwise from the north direction. Below, the bearing of B from A is 025 degrees (note 3 figures are always given). The bearing of A from B is 205 degrees. Example A, B and C are three ships. The bearing of A from B is 045º. The bearing of C from A is 135º.